Distinguishing between power cables and control cables requires attention to the following points
Power cables are used for transmitting and distributing electrical energy. They are commonly used in urban underground power grids, power plant outgoing lines, external power supply for industrial and mining enterprises, and cross-river and underwater power transmission lines. Power cables are cable products used to transmit and distribute high-power electrical energy in the main branch lines of the power system. They include various voltage levels from 1 to 500 kV and above, and various insulated power cables. Control cables are polyvinyl chloride insulated and sheathed control cables suitable for use in industrial and mining enterprises, power transportation departments, and places where AC rated voltage is below 450/750 volts for control and protection lines. Both have similar structures, but their uses are vastly different, requiring careful distinction during use.
To distinguish between power cables and control cables, pay attention to the following points:
1. Check the rated voltage. The rated voltage of power cables is generally 0.6/1 kV and above, while control cables are mainly 450/750 V.
2. Check the thickness of the insulation and sheath. In the production of unusually specified power cables and control cables, the insulation and sheath thickness of power cables are thicker than those of control cables.
3. Check the implementation standards on the control cable. Control cables belong to electrical equipment cables, and are two of the five major categories of cables. The standard for power cables is GB12706, and the standard for control cables is GB/T9330. Control cables should also meet the technical conditions of the IEC337-8 standard.
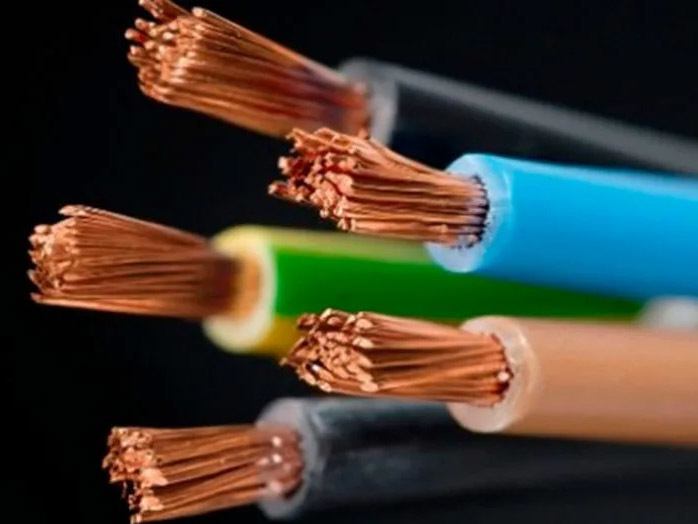
4. Check the color of the insulated core wires. The insulation sleeves of each inner core of high-voltage power cables are generally color-coded; while the insulated core wires of control cables are generally black with white lettering.
5. Check the cross-section of the control cable. Power cables primarily transmit power and generally have a large cross-section, while the cross-section of control cables generally does not exceed 10 square millimeters. The specifications of power cables can generally be larger, up to 500 square millimeters (the range that conventional manufacturers can produce); while the cross-section of control cables is generally smaller, generally not exceeding 10 square millimeters.
6. Check the number of cable cores. In terms of the number of cable cores, power cables generally have a maximum of 5 cores according to grid requirements, while control cables transmit control signals and have more cores. According to standards, there are as many as 61 cores, but they can also be produced according to user requirements.
Tag:
Previous Page
Previous Page:
Recommended News
Methods for testing the insulation strength of insulated wires and cables
Distinguishing between power cables and control cables requires attention to the following points
Xingzhou Cable explains the difference between flame-retardant cables and fire-resistant cables